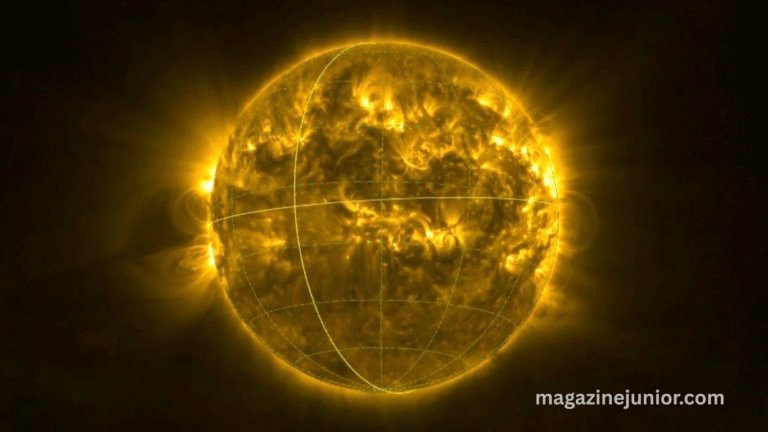
For the first time in human history, a European spacecraft has captured astonishing images of the sun’s elusive south pole. These groundbreaking visuals are offering scientists an entirely new perspective on the sun, unlocking secrets that have long been hidden from direct observation.
Understanding the sun’s poles is crucial because they play a significant role in shaping the solar magnetic field, which in turn influences space weather, satellite safety, and even power grids on Earth. For decades, astronomers have faced limitations, as existing technology has been unable to access these mysterious regions directly, leaving critical gaps in solar knowledge.
In this article, readers will explore the remarkable journey of the mission, the technology behind these images, the potential scientific breakthroughs, and the global implications of observing the sun’s south pole. This monumental achievement marks a significant milestone in solar research, offering new hope for predicting and mitigating solar threats.
The Solar Orbiter’s Mission and Objective
The European Space Agency’s Solar Orbiter embarked on its mission with one central goal: to provide unprecedented views of the sun’s polar regions. Launched in February 2020, the spacecraft traveled millions of kilometers, using intricate gravitational assists from Venus to tilt its orbit and position itself optimally.
Its advanced instruments are designed to endure intense solar radiation while capturing high-resolution images and data. By focusing on the sun’s south pole, the Solar Orbiter enables scientists to observe solar dynamics that have been hidden due to Earth’s limited orbital perspective.
Unveiling the Sun’s Hidden South Pole
The south pole of the sun has mainly remained uncharted because most spacecraft view the sun from the ecliptic plane. The Solar Orbiter’s maneuver allowed it to break free from this constraint and capture direct images never seen before.
These images reveal complex magnetic structures, swirling plasma, and dynamic activity that could help explain solar phenomena, such as the eleven-year solar cycle and magnetic reversals. Observing these features in real-time offers vital clues about the behavior of solar storms and their potential impact on Earth.
The Importance of Studying Solar Poles
The sun’s poles govern much of its magnetic activity, which directly influences space weather patterns. Solar flares, coronal mass ejections, and magnetic storms originate from the sun’s magnetic field, which is heavily influenced by polar activity.
Read More : Trump’s financial disclosures reveal tens of millions in income from guitars
Accurately observing these regions allows scientists to refine their models and forecasts. This understanding could lead to better predictions of solar storms that threaten satellites, astronauts, communication systems, and global power infrastructure.
How Solar Orbiter Overcame Technical Challenges
Capturing images of the sun’s poles presented unique engineering challenges. The spacecraft had to endure extreme temperatures and intense radiation and operate its instruments with precision under harsh solar conditions.
The design incorporated advanced heat shields, high-gain antennas, and innovative cooling systems. Instruments like the Polarimetric and Helioseismic Imager (PHI) and Extreme Ultraviolet Imager (EUI) were specifically calibrated to function accurately in this volatile environment, ensuring the integrity of the data collected.
Early Discoveries and Unexpected Findings
Initial observations have already yielded surprising results. Complex jet-like structures and rapid magnetic field shifts observed at the south pole challenge previous assumptions about solar activity.
These findings suggest that the sun’s poles may have a more active role in driving solar phenomena than previously believed. Early data points toward the possibility of previously unknown mechanisms influencing the solar cycle and the generation of solar winds.
Global Scientific Collaboration Behind the Mission
The Solar Orbiter mission represents a monumental collaboration between the European Space Agency, NASA, and numerous scientific institutions worldwide. Hundreds of researchers, engineers, and mission specialists contributed to its design, execution, and ongoing analysis.
This global partnership highlights the shared human ambition to understand the universe. Such cooperative efforts not only advance science but also foster international unity in the face of common challenges posed by cosmic forces.
Potential Implications for Earth and Future Research
The knowledge gained from these images holds significant implications for Earth. By improving our understanding of the sun’s magnetic dynamics, researchers can enhance forecasting models, providing earlier warnings of potentially damaging solar storms.
Looking ahead, these observations could guide future missions aimed at even closer and more detailed exploration. Insights from the South Pole may also influence the design of space travel technologies, ensuring greater safety for astronauts and spacecraft operating in solar proximity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Solar Orbiter?
The Solar Orbiter is a European spacecraft launched in 2020 to study the sun’s polar regions and gather data on its magnetic activity.
Why focus on the sun’s south pole?
The sun’s poles are crucial to understanding its magnetic field, solar cycle, and space weather effects on Earth, making direct observation vital.
How did the Solar Orbiter capture these images?
The spacecraft used gravitational assists and specialized instruments to tilt its orbit and directly observe the south pole for the first time.
What makes these images historic?
These are the first high-resolution images of the sun’s south pole, revealing never-before-seen magnetic structures and plasma dynamics.
How do solar poles affect Earth?
The sun’s polar activity influences space weather, which can impact satellites, communication systems, navigation, and power grids on Earth.
What challenges did the mission face?
Engineers overcame extreme heat, radiation, and technical precision requirements to ensure successful data collection from the sun’s poles.
Who collaborated on the mission?
The mission involved cooperation between the European Space Agency, NASA, and international scientific communities.
What future benefits can this research offer?
Improved solar storm forecasting, better protection for space assets, enhanced scientific models, and safer space exploration missions are expected outcomes.
Conclusion
The European probe’s capture of the sun’s south pole images marks a historic breakthrough in solar science. By revealing hidden magnetic structures and plasma dynamics, the mission advances the understanding of solar behavior. This achievement results from global collaboration and cutting-edge technology and offers crucial insights for predicting solar storms, safeguarding satellites, and ensuring future space exploration.